Info
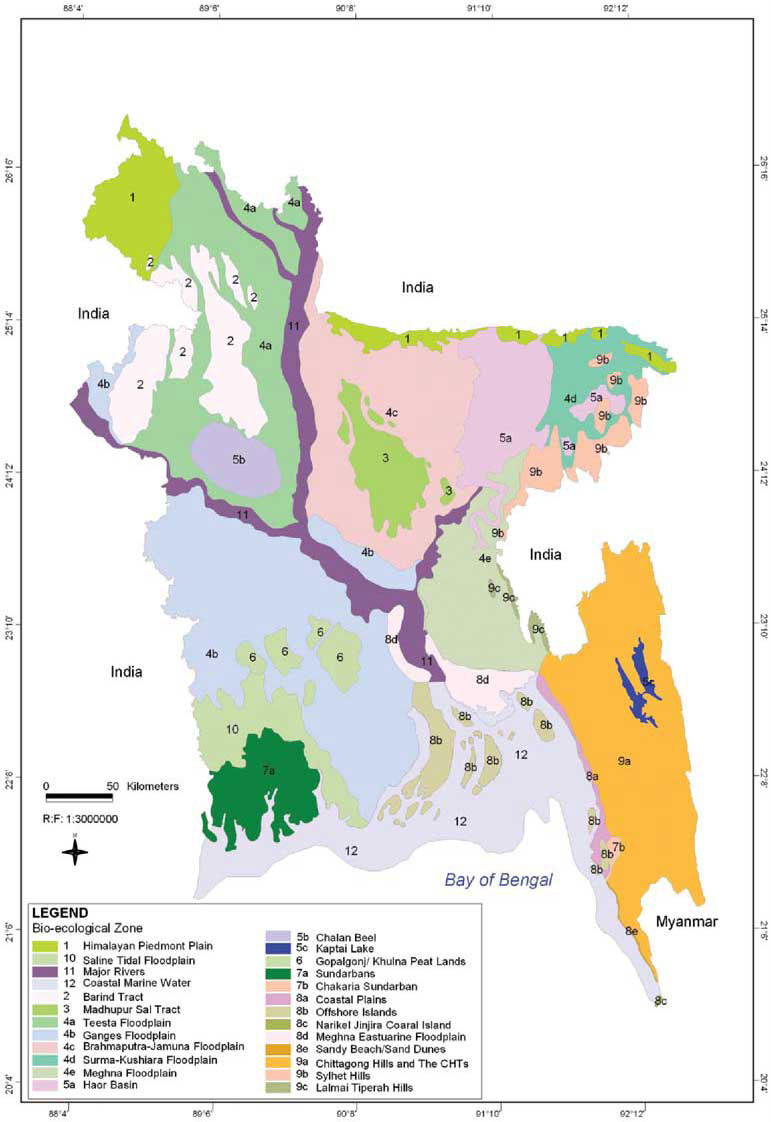
Bangladesh is situated in the “oriental region”, between the Indo-Himalayas and Indo-Chinese subregions. The country has a total area of 147,570 km , of which about 80 percent comprises one of the largest deltaic plains in the world, formed in the confluence of the Ganges, the Brahmaputra (Jamuna), and theMeghna rivers. The remaining 20 percent of the land area is comprised of the undulating, forested Hill Tracts. Distinct physiographic characteristics, variations in hydrological and climatological conditions, and difference in the soil properties in Bangladesh contribute in developing diverse forms of ecosystems enriched with great diversity of flora and fauna.
Diversity of ecosystems and its rich floral and faunal resources havemade Bangladesh and its ecosystems resilient to natural calamities. The rich biodiversity of this land with moderate tropical climate makes it soothing for the human habitation. As an agrarian society, Bangladesh and its population heavily depends on the genetic resources of crop varieties.The history of its rich agricultural practices goes back to many centuries and farmers were highly innovative to create many cultivars using wild genetic resources. Presence of 10,000 plus rice varieties is a clear example of our vast wealth of genetic resources. Bangladesh is also one of the oldest producers of cotton and its rich and diverse collection of medicinal plants attracts attentions throughout the history.
The Ecosystem Diversity of Bangladesh is divided in the following categories:
- Forest Ecosystem
- State of Wetlands Ecosystem
- Homestead Ecosystem
- Coastal and Marine Ecosystem
- Agro-ecosystem